Published Jan 25, 2023
Definitive proof that choosing refurbished helps the planet
We started Back Market knowing that refurbished tech is better for the environment than brand new but without a clear idea of exactly how much better. We also knew that gaining a concrete and data-driven understanding of the environmental impact of refurbished tech was key to our mission.
That’s why we asked ADEME, the French Environment and Energy Management Agency, to study the environmental impact of the refurbished tech industry. The question of impact is important globally, not just to Back Market — because of this, ADEME decided to launch the first-ever large-scale study on the environmental impact of refurbished tech. (Back Market did not sponsor the study in any way.)
In 2020, ADEME began their research, and in January 2022, they released preliminary data surrounding the environmental impact of refurbished tech, centering on smartphones. Their conclusion was clear: Refurbished smartphones have significantly less impact on the environment compared to brand new.
Now, the full ADEME report has been released, giving us a big-picture view of the global impact of refurbishing tech – specifically computers, tablets, desktops, and smartphones. This study did not include the analysis of monitors, keyboards, and mice.
Methodology
The 2022 ADEME report was conducted using the Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology, also referred to as Life Cycle Analysis.
LCA methodology assesses the environmental impact of a product, process, or service by examining all stages of the life cycle. It’s considered a holistic approach. In this case, LCA methodology was applied to laptops, desktop computers, smartphones, and tablets, evaluating the entire value chain of a device from new to refurbished.
Factors evaluated for new devices
Raw materials and their extraction
Component production
Upstream transport
Manufacturing process
Production of packaging and accessories
Distribution
Use
End-of-life (incineration or landfill disposal)
Factors evaluated for refurbished devices
Collection of used devices
Manufacturing of spare parts
Destruction of used spare parts
Production of packaging and accessories
Shipping
These factors were evaluated on a global scale, making this data applicable worldwide
Environmental KPIs
The report takes into account numerous key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of refurbishment (as well as new manufacturing) on the environment.
ADEME’s report covers the following 4 types of environmental impact:
Carbon footprint
Raw materials (this includes metals extracted from the earth, as well as fossil fuels burnt during the extraction process)
Water consumption
E-waste generation
Device-use scenarios
The impact of refurbishment also depends on the time the device is used before being refurbished (aka its “first life”), and the estimated length of its second (refurbished) life.
We call these device-use scenarios.
The average device-use scenario assumes that the refurbished product has been purchased as new, used for a certain amount of time, refurbished, then used for a certain amount of time again.
The study assumed the following averages:
Smartphones and tablets: 3 years of use as a new device, 2 years of use as a refurbished device
Computers (laptops and desktops): 5 years of use as a new device, 3 years of use as a refurbished device
Please note that these are conservative device-use scenarios, so as to avoid the risk of overstating the environmental benefit of refurbishment.
Repair scenarios
Part of a device’s impact is the location or locations where it is sourced, repaired, and sold. For example, it’s rare for a device to be sourced, repaired, and sold in the same country. The report integrated 3 scenarios, from “worst” to “best” in terms of environmental impact:
Worst case scenario: a device is sourced in one country, refurbished in a second, and sold in a third, with a significant number of parts replaced.
Average scenario: a device is either sourced, refurbished, or sold in two different countries, with an average number of parts replaced.
Best case scenario: a device is sourced, refurbished, and sold in the same country, with an average (or less) number of parts replaced.
Please note: the average scenario is the most representative of the majority of devices sold on Back Market.

For laptops and desktop computers, the hard disk is the highest-impact replacement for both computers and laptops because the production that goes into creating a new hard disk is incredibly resource-heavy. And as with smartphones and tablets, a battery replacement also greatly impacts the environment.
Note: this study did not include the analysis of monitors, keyboards, and mice.

Refurbished tablets and smartphones vs. brand new
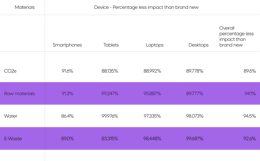
The environmental impact of refurbished smartphones compared to brand new smartphones, by the numbers.
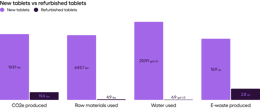
The environmental impact of refurbished tablets compared to brand new tablets, by the numbers.
Impact — smartphones and tablets
The most impactful step of a refurbished device’s life on the environment is the refurbishment process. The more parts that must be replaced to renew the device, the higher the environmental impact.
Screens and batteries have the highest environmental impact of all part replacements. For batteries, this is because they require lithium, and extracting lithium is an environmentally costly process.
Another driver of environmental impact is e-waste. When manufacturers provide accessories, like a charging cable, the amount of e-waste associated with the tablet or smartphone increases.
While there are variations between the ranges of scenarios presented above, refurbished smartphones and tablets will always have less of an impact on the environment than new. Even with the inclusion of resource-heavy replacement parts, like batteries, refurbished devices significantly lessen environmental impact. And with 5 billion smartphones thrown away in 2022, we’ve already extracted more than enough material from the planet to renew countless devices.
Refurbished laptops and desktop computers vs. brand new
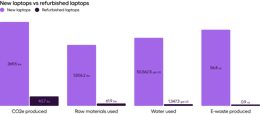
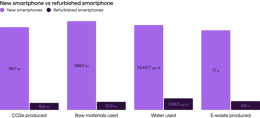
The environmental impact of refurbished laptops compared to brand new laptops, by the numbers.
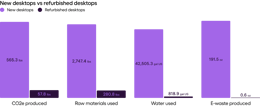
The environmental impact of refurbished desktop computers compared to brand new desktop computers, by the numbers.
Impact — laptops and desktop computers
Compared to smartphones and tablets, laptops and desktops often need fewer parts replaced — but when they do, the impact is much higher. This is due to the environmental impact of manufacturing hard disks. As with smartphones and tablets, battery replacement also has a significant environmental impact. The production of these parts is responsible for the majority of a brand-new laptop or desktop’s environmental impact, so when refurbished laptops and desktop computers require those same parts, the environmental impact of refurbished and brand new is similar.
If multiple major parts are needed during the refurbishment process (disk, screen, RAM) and the computer is used less than 5 years before being refurbished, then the benefit of refurbishment to the environment is lost. The hard disk is the highest-impact replacement for both computers and laptops because the production that goes into creating a new hard disk is incredibly resource-heavy. And as with smartphones and tablets, a battery replacement also greatly impacts the environment. However, within the range of scenarios, there is good news: If fewer replacement parts are needed, or if replacement parts are sourced second-hand, the positive impact of refurbishment on the environment is preserved.
Overall Conclusion
We know it was a long read, but we hope it was worth it. The data obtained by ADEME is incredibly encouraging for the future of refurbished electronics.
This study makes it clear — refurbished tech is better for the planet than brand new at almost every turn. Even with the higher-impact part replacements, the vast majority of refurbished devices have significantly less of an impact on the environment.
This is important because tech isn’t going anywhere — literally. From work to play, these devices are an integral part of our world. Instead of letting our old tech waste away in a landfill, we can make a choice to get the most out of these devices while giving the planet a break. It means that we can make a choice in our day-to-day lives that have a positive effect on the environment
To sum it up:
The longer you use your device, the better
Refurbished smartphones and tablets always avoid a significant amount of environmental damage when compared to brand new smartphones and tablets
Refurbished laptops and desktops almost always avoid a significant amount of environmental damage when compared to brand new, except when significant part replacements are required, like hard disks.